What is Nail Intramedullari and How is it Used in Surgery?
nail intramedullari is a crucial technique in modern surgery. It involves inserting a rod into the medullary cavity of bones. This method is primarily used for stabilizing fractures and aiding recovery. It acts like a natural support for the bone structure.
Surgeons utilize Nail Intramedullari in various scenarios. The procedure promotes healing and allows for early mobility. However, challenges exist. For instance, infection or improper placement of the nail can lead to complications. Surgeons must be precise.
Patients often wonder about the effectiveness of Nail Intramedullari. Many report improved outcomes. Yet, the experience may vary. Some face unexpected side effects, which require further consideration. Understanding this technique is vital for patients and medical professionals alike.
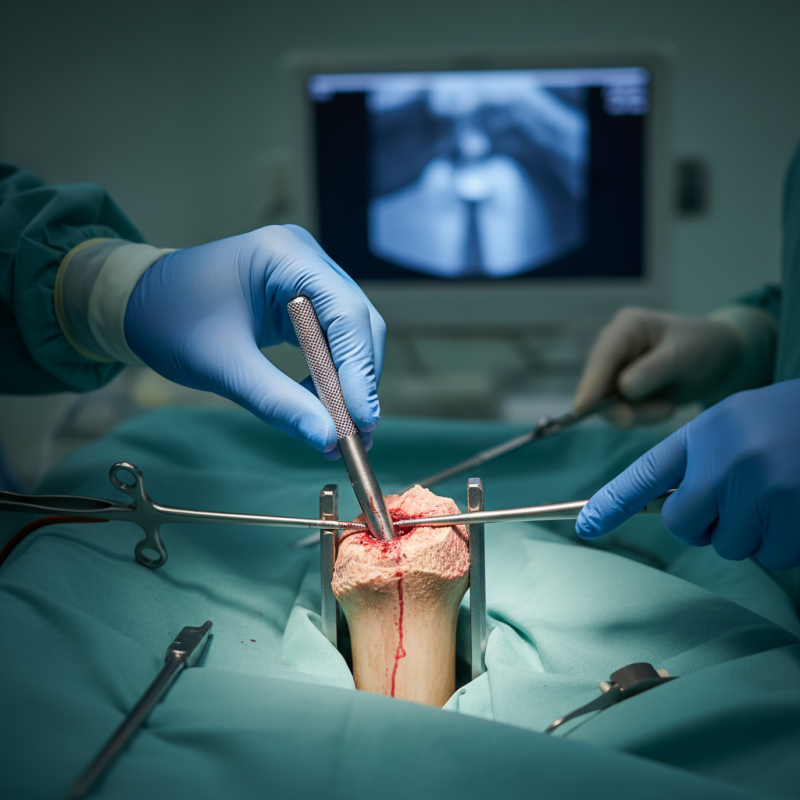
What is Nail Intramedullari? Definition and Overview
Nail intramedullari, or intramedullary nail, is a surgical tool used in orthopedic procedures. It is primarily utilized to stabilize fractures within long bones. The nail is inserted into the medullary cavity of the bone, providing support from the inside. This technique aims to promote healing while allowing for better mobility post-surgery.
Surgeons often choose this method for complex fractures. The design of the nail allows for minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. This can lead to quicker recovery times, yet it doesn't eliminate all risks. Complications such as infection or improper alignment can still occur. It's crucial for surgeons to assess each fracture's unique characteristics before proceeding.
While the benefits are significant, challenges remain. Not every patient responds similarly to this treatment. Some may experience discomfort or functional limitations later on. Also, the need for follow-up procedures is not uncommon. It highlights the importance of thorough pre-operative evaluations and patient education. Each case requires careful consideration and reflection on potential outcomes.
What is Nail Intramedullari and How is it Used in Surgery?
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Nail Intramedullari, or intramedullary nail, is a metal rod inserted into the medullary cavity of a bone to stabilize fractures. |
| Indications | Used primarily for long bone fractures, particularly in the femur and tibia. |
| Types | There are various types including antegrade, retrograde, and locked intramedullary nails. |
| Surgical Technique | Typically involves reaming the bone canal, inserting the nail, and securing it with screws. |
| Benefits | Promotes early mobilization and provides stable fixation, which can enhance healing. |
| Risks | Potential complications include infection, non-union, and malalignment. |
| Recovery | Recovery time varies, but patients generally can bear weight within weeks depending on the fracture type and location. |
Historical Development of Intramedullary Nails in Surgical Practice
Intramedullary nails have a rich history in surgical practice, dating back to the early 20th century. Initially used for stabilizing fractures, this technique has evolved significantly. The 1970s marked a turning point with advancements in materials and design. Reports show a decrease in complication rates from 25% to 5% over this period. These nails improved the healing process and allowed for earlier mobilization of patients.
Tips: Always assess the type of fracture before choosing the nail design. This could influence recovery times. Understanding the specific anatomy is crucial for successful application.
The growth of intramedullary nailing reflects shifts in surgical philosophy. Surgeons began to favor internal fixation over external methods. Despite its advantages, challenges remain. Some patients still experience discomfort or complications post-surgery. Research indicates that around 15% of patients report dissatisfaction due to persistent pain. This suggests a need for better patient selection and improved techniques.
Tips: Communicate openly with patients about potential risks. They should understand both the benefits and limitations of the procedure. A well-informed patient is often more compliant and satisfied.
Key Types of Intramedullary Nails and Their Applications in Orthopedics
Intramedullary nails are vital in orthopedic surgery. They stabilize fractured bones by being inserted into the medullary cavity. This method is less invasive and promotes faster healing. Surgeons often choose different types of intramedullary nails based on the patient’s needs and the type of fracture.
There are several key types of intramedullary nails. One common type is the femoral nail, which supports the thigh bone. Another is the tibial nail, used for fractures in the shin. Both types offer various locking mechanisms. These mechanisms help in maintaining bone alignment. However, each type has limitations and may pose challenges during insertion.
Surgeons must carefully evaluate these options. Not all nails are suitable for every patient. Fracture complexity and bone quality are significant factors. Despite advancements, issues like non-union still occur. This indicates the need for ongoing assessment and improvement. Effectively utilizing intramedullary nails requires experience and a personalized approach for each case.
Technical Considerations in the Surgical Insertion of Intramedullary Nails
Intramedullary nails are commonly used in orthopedic surgery to treat fractures. The surgical insertion process is crucial for effective healing. Several technical considerations must be taken into account during this procedure. For example, proper alignment of the nail is essential to ensure stability. Accurate entry point selection can significantly influence the outcome. Surgeons often face challenges with misalignment. This can lead to delayed recovery or complications.
Tip: Always ensure the nail length matches the bone size. This prevents unnecessary stress on surrounding tissues.
Another aspect to consider is the patient's anatomy. Each individual has unique skeletal structures that can complicate the insertion. Surgeons should use imaging techniques to guide their placement. This approach can help avoid errors. Misplacement can result in malunion or nonunion of the fracture.
Tip: Communication with the patient about their specific anatomy is key. This helps prepare both surgeon and patient for potential complications.
Ultimately, successful intramedullary nail insertion requires precision, adaptability, and an understanding of each case's complexities. No two surgeries are the same, and reflection on past challenges can lead to improved techniques.
Outcome Metrics: Success Rates and Complications in Nail Intramedullari Usage
Nail intramedullari is a surgical technique used to stabilize fractures. It involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary canal of a bone. This technique is commonly applied to long bones, such as the femur and tibia. Surgeons often use it for its minimal invasiveness and the ability to facilitate faster healing.
Success rates for nail intramedullari procedures are generally high. Many studies highlight rates around 90% for stable fractures. However, complications can arise. Common issues include infection, malunion, and hardware failure. Patients may experience discomfort at the site of insertion. It’s essential for patients to understand these potential risks before opting for the surgery.
Tips for managing recovery after surgery include regular follow-up appointments. Monitoring for signs of infection is crucial. A warm sensation or unusual discharge at the incision site should be reported immediately. Physical therapy can greatly enhance the recovery experience. Engaging in light exercises as recommended by healthcare providers promotes better outcomes and muscle strength.
Nail Intramedullari Surgical Outcomes
This chart illustrates the success rates and complications associated with Nail Intramedullari usage in surgical procedures. The data includes the percentage of successful outcomes compared to various complications observed.